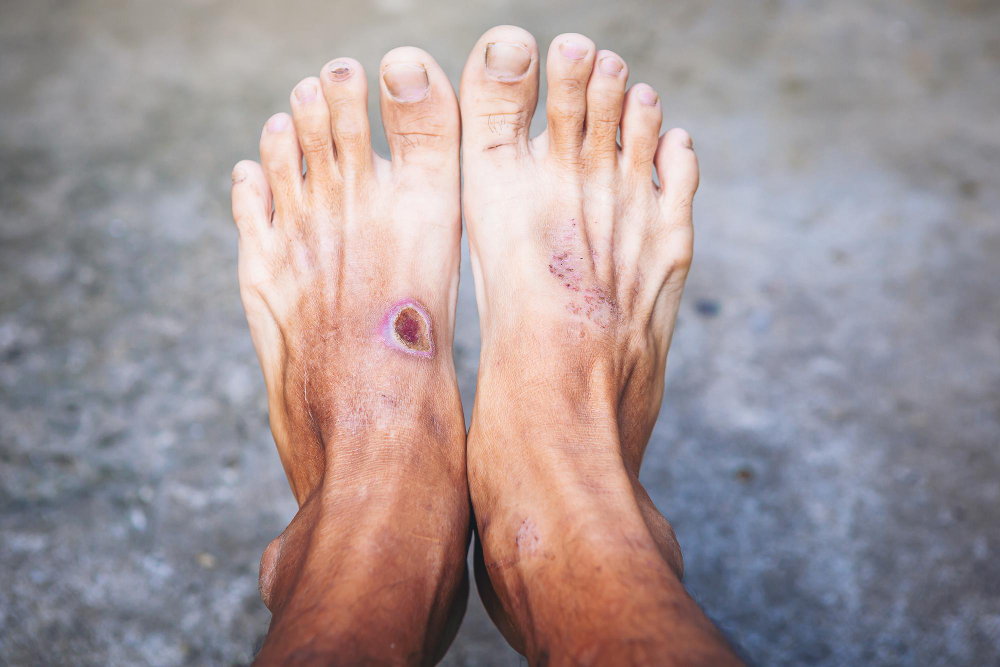
What is Gangrene in Diabetic Feet?
Gangrene in diabetic feet is a serious condition. It happens when tissue in the foot dies due to poor blood flow or infection. People with diabetes are at higher risk for foot problems. This includes diabetic foot complications like foot infection in diabetes. If not treated quickly, gangrene can lead to amputation. Therefore, preventing gangrene in diabetes is very important for your health and safety.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Early signs of gangrene in diabetic feet can be easy to miss. However, knowing what to look for can help you act fast. Watch for these symptoms:
If you notice any of these signs, seek medical help right away. Quick action can save your foot and your health.
Causes and Risk Factors
Gangrene in diabetic feet often starts with a small injury or sore. Because diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, even minor cuts may not heal well. As a result, infections can develop quickly. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
Additionally, people with diabetes for many years have a higher risk. Smoking and kidney disease can also increase your chances of gangrene.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Doctors use several steps to diagnose gangrene in diabetic feet. First, they will check your foot for color changes, wounds, and signs of infection. Next, they may order tests such as:
Early diagnosis is key. Therefore, regular foot exams are important for anyone with diabetes. According to the CDC, checking your feet daily can help catch problems early.
Treatment Options
Treating gangrene in diabetic feet depends on how severe the problem is. Doctors may use one or more of these treatments:
With early care, many people recover without losing their foot. However, waiting too long can make treatment harder.
Prevention and Foot Care Tips
Preventing gangrene in diabetes is possible with good foot care. Here are some tips to keep your feet healthy:
In addition, if you live in a city with high diabetes rates, look for diabetic foot care in your area. Many clinics offer special foot checks for people with diabetes.
When to See a Doctor
If you have diabetes, do not ignore any changes in your feet. See a doctor right away if you notice:
Early treatment can prevent serious problems. Therefore, regular check-ups are important for everyone with diabetes.
If you have diabetes and notice any foot changes, consult a specialist at HS Hospital for personalized guidance. Your quick action can protect your health and prevent serious complications.