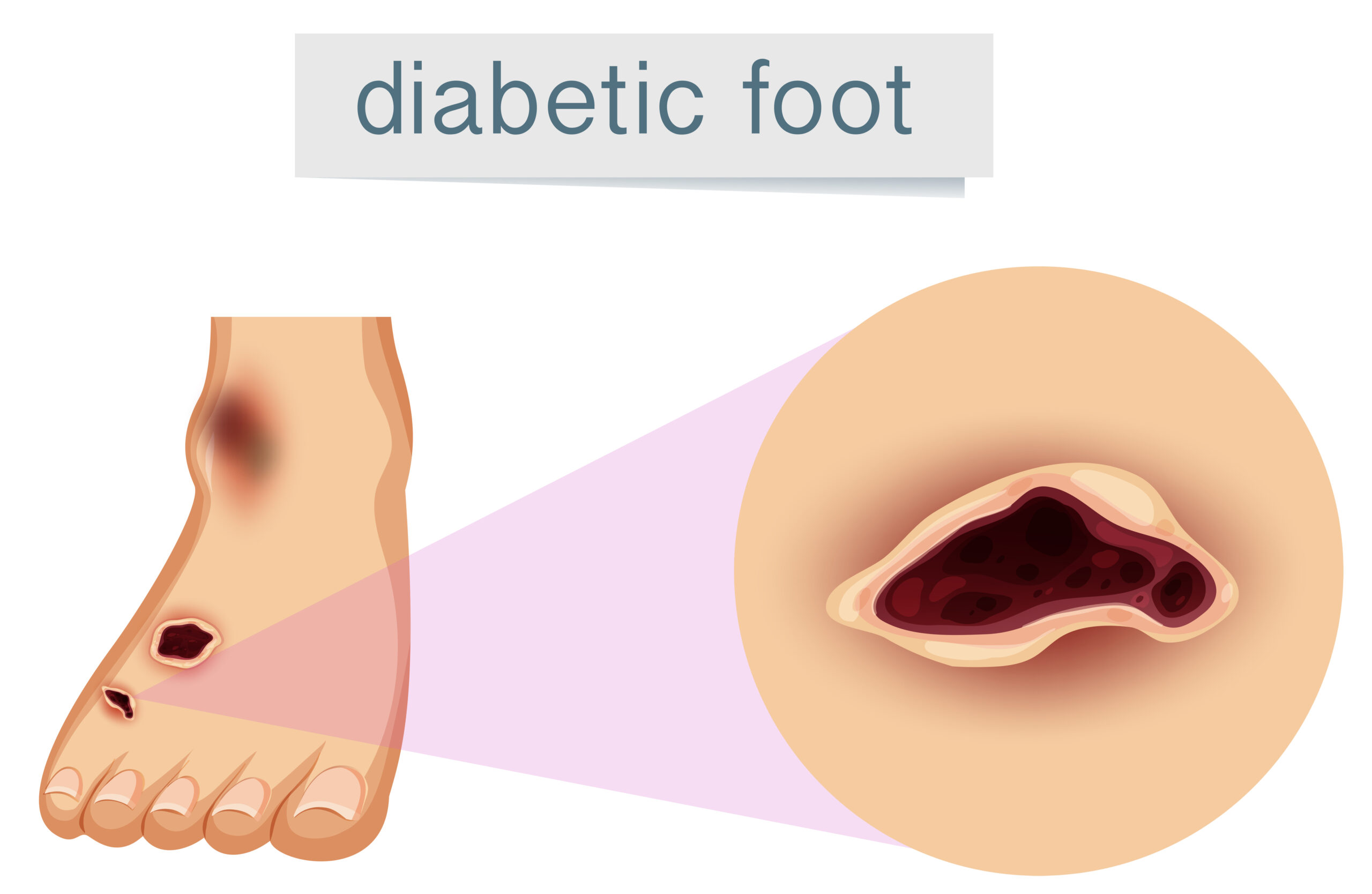
What Is Diabetic Foot?
Diabetic foot is a common problem for people with diabetes. It happens when high blood sugar damages nerves and blood vessels in the feet. As a result, you may not feel pain or injuries. Over time, small cuts or sores can turn into serious wounds. Because of this, diabetic foot needs careful attention. Early care can help prevent problems and keep your feet healthy.
Common Symptoms of Diabetic Foot
It is important to know the signs of diabetic foot. Early symptoms can be mild, but they may get worse if ignored. For example, you might notice:
If you see any of these diabetic foot symptoms, you should act quickly. Early treatment can stop problems from getting worse.
Causes and Risk Factors
Diabetic foot develops because of nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood flow. Both are common in people with diabetes. However, some factors can raise your risk even more. These include:
Because of these risks, regular foot checks are very important. Even small injuries can become serious if not treated early.
How Diabetic Foot Is Diagnosed
Doctors use several steps to diagnose diabetic foot. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they examine your feet for cuts, sores, or changes in color. Often, they check your foot pulses to see if blood flow is normal. In some cases, doctors may use special tests, such as:
Because early diagnosis helps prevent serious issues, regular foot exams are key for people with diabetes.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Foot
Diabetic foot treatment depends on the problem’s severity. Early care can prevent complications. Common treatments include:
Because each case is different, your doctor will choose the best diabetic foot treatment for you.
Prevention and Daily Care Tips
Preventing diabetic foot problems is possible with daily care. Here are some diabetic foot care tips:
Because prevention is easier than treatment, follow these steps every day. If you wonder how to prevent diabetic foot, these habits are a good start.
When to See a Doctor
Sometimes, problems can develop quickly. You should see a doctor right away if you notice:
Because fast action can save your foot, do not wait if you see these signs. Early treatment can prevent serious problems.
For more information, consult trusted sources like the CDC and WHO. They offer helpful advice on diabetic foot care and prevention.
Consult a specialist at HS Hospital for personalized guidance on diabetic foot care.